LANs
Description:
LANs are Local Are Networks or Internal Networks- The entire network in a building or multiple buildings where all devices need to communicate with each other, but do not have to communicate with the internet or devices outside the network. The easiest way to picture a LAN is a self contained house. All the rooms represent the internal devices, the hallways represent the paths the data flows throughout the LAN, and the walls/ doors prevent data from reaching outside the house. For a multi-building LAN, just picture a house with a hallway that connects to another house directly and includes all of it’s rooms on the “internal network”. You do not need a router or modem to connect a LAN, a hub or switch is all that is needed. Hubs are rarely used anymore because they re-broadcasts every signal they get making them multi-port repeaters, so you will most likely see switches.
Typical Network Setup:
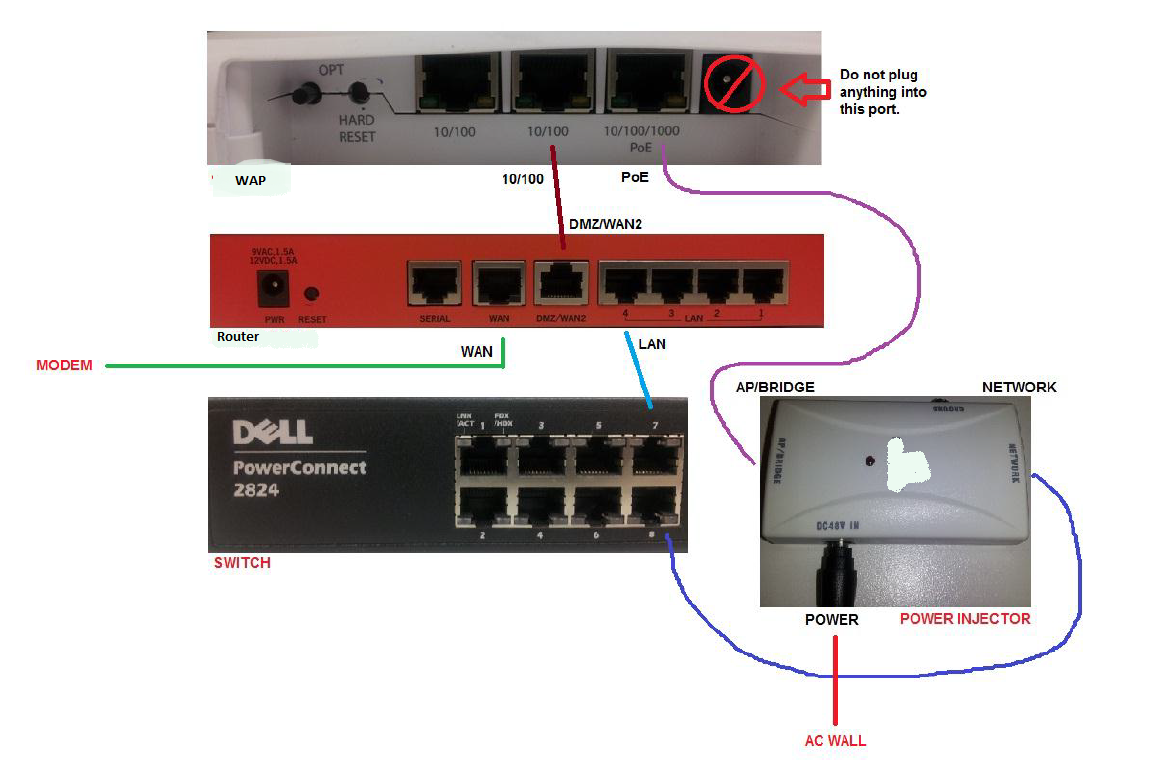
- Note: MAKE SURE THE MODEM AND ROUTER ARE ON SEPARATE SUBNETS!!
-
There should be no cables going out of the modem except ONE from one of the ethernet ports to the WAN port on the router as in the diagram.
-
Anything on the internal network should connect to any of the numbered LAN ports on the router. You can also “daisy chain” switches for larger networks, although a larger switch would be a better option.
-
This particular WAP can do both an internal AND an external wireless for the network. A typical WAP can only do one so you would place it on any of the LAN ports on the router or port on a switch if you want it for internal network only and on the WAN2/DMZ on the router if you want it to be external wireless only.
Most Networking Issues Can Be Resolved By Checking:
-
Firewalls => Firewalls need to be disabled for the internal network to allow free flow of information.
-
Antivirus Software => Antivirus software can have components that interfere with networking. Look especially for “Identity Protection” or “Firewall” components.
-
Network Connections => Always check your network settings for configuration settings.
-
Ping Tests => This one is most useful. Ping the Default Gateway and other nodes on the network to see the point of failure. Go from the internal network out to the internet.
NIC Settings Should Look Like:
- IP Address => 192.168.1.70 => Servers are almost always .10 / Printers .11 => .29 / Workstations are .30-.70 / WAP’s .100 => .254
- Subnet Masks => 255.255.255.0 => Typical Class C Network that allows up to 254 nodes.
- Default Gateway => 192.168.1.1 => This is the router’s IP Address.
- Primary DNS => 192.168.1.1 => This needs to be the IP Address of the DC (Domain Controller) if on a Domain. If not, the router’s IP Address.
- Secondary DNS => 8.8.8.8 => (Google’s DNS Servers) There will be no secondary DNS when the DC is the primary DNS.
For Most System Wide Networking Issues:
- Have the customer power cycle their networking equipment. Power on in this order: Modem, Router, and Switch.
Comments